Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tei, C.; Otaka, Masahiko; Kuwahara, Daisuke*
Chemical Physics Letters, 829, p.140755_1 - 140755_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)We were able to detect the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal of a liquid sodium clinging to the interface of solid metal particles for the first time. In this study, we confirmed the difference in the relaxation times due to the difference in the interactions between liquid sodium and metal particles suspended in the liquid sodium. It was found that the surface of the micro titanium particles and liquid metallic sodium interact physically, not chemically.
Matsuda, Shohei; Nakashima, Nobuaki*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Taniguchi, Seiji*; Chosrowjan, H.*; Somekawa, Toshihiro*; Yatsuhashi, Tomoyuki*
Chemical Physics Letters, 802, p.139759_1 - 139759_6, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Hirade, Tetsuya; Michishio, Koji*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Oshima, Nagayasu*
Chemical Physics Letters, 795, p.139507_1 - 139507_4, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)We obtained the temperature dependence up to 150 C of the triplet positronium (
C of the triplet positronium (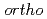 -Ps) lifetime in N,N,N-Trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI) by the vertical slow positron beamline installed at AIST. Positrons penetrate into the liquid surface of TMPA-TFSI with the positron energies of 2 keV and 12 keV to investigate at the near-surface and the balk. The surface structure was visible at 150
-Ps) lifetime in N,N,N-Trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI) by the vertical slow positron beamline installed at AIST. Positrons penetrate into the liquid surface of TMPA-TFSI with the positron energies of 2 keV and 12 keV to investigate at the near-surface and the balk. The surface structure was visible at 150 C, 120
C, 120 C above the melting temperature. The
C above the melting temperature. The 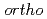 -Ps lifetime became shorter at higher temperatures for both positron energies. Similar temperature dependence had appeared just in water as the result of the reaction of
-Ps lifetime became shorter at higher temperatures for both positron energies. Similar temperature dependence had appeared just in water as the result of the reaction of 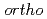 -Ps and radiolysis products such as the OH radicals. The temperature dependence observed for TMPA-TFSI suggested that the chemical reaction of
-Ps and radiolysis products such as the OH radicals. The temperature dependence observed for TMPA-TFSI suggested that the chemical reaction of 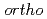 -Ps occurred.
-Ps occurred.
 molecular dynamics simulations using the SCAN meta-GGA density functional and EXAFS spectroscopy studies
molecular dynamics simulations using the SCAN meta-GGA density functional and EXAFS spectroscopy studiesYamaguchi, Akiko; Kobayashi, Keita; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Chemical Physics Letters, 780, p.138945_1 - 138945_5, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:44.89(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Nakashima, Nobuaki*; Yatsuhashi, Tomoyuki*; Sakota, Kenji*; Iwakura, Izumi*; Hashimoto, Sena*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Matsuda, Shohei
Chemical Physics Letters, 752, p.137570_1 - 137570_5, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5(Chemistry, Physical)Photo-redox reactions between Eu and Eu
and Eu ions are induced by laser irradiation in alcoholic solution. Efficiency, wavelength dependence, and laser-power dependence are investigated with three different lasers. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 308 nm is found to cause one-photon redox reactions with a quantum yield around 0.5. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 394 nm induces two-photon reduction of Eu
ions are induced by laser irradiation in alcoholic solution. Efficiency, wavelength dependence, and laser-power dependence are investigated with three different lasers. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 308 nm is found to cause one-photon redox reactions with a quantum yield around 0.5. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 394 nm induces two-photon reduction of Eu to form Eu
to form Eu . When the pulse energy is 5 mJ, the quantum yield is measured to be 0.015. Although the quantum yield is one order of magnitude lower than that of the one photon reduction, reduction phenomena can be easily observed under the moderate laser field strength. Because of the two-photon nature, there should be a room to improve the efficiency by increasing the laser field strength.
. When the pulse energy is 5 mJ, the quantum yield is measured to be 0.015. Although the quantum yield is one order of magnitude lower than that of the one photon reduction, reduction phenomena can be easily observed under the moderate laser field strength. Because of the two-photon nature, there should be a room to improve the efficiency by increasing the laser field strength.
Yonetani, Yoshiteru*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi
Chemical Physics Letters, 749, p.137441_1 - 137441_5, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)We calculated solvent accessibility of DNA backbone hydrogen sites, H1'-H5' by using molecular dynamics simulation of DNA. The result of accessibility is well correlated with the site-dependent reactivity with OH radicals experimentally reported, indicating that the different DNA-radical reactivity is mainly caused by the difference in the solvent accessibility of each hydrogen site. Compared with the previous calculation with solvent-accessible surface area, the present MD-based counting of molecular access provided a slightly improved result, which suggests importance of more realistic molecular components such as electrostatic interactions and DNA conformational fluctuation.
 , K
, K , and Na
, and Na in gas and aqueous phases
in gas and aqueous phasesSuno, Hiroya; Machida, Masahiko
Chemical Physics Letters, 730, p.26 - 31, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.21(Chemistry, Physical)We perform quantum chemical calculations for the Cs , K
, K , and Na
, and Na complexes of norbadione A (NBA), a pigment molecule in mushrooms known to accumulate Cs
complexes of norbadione A (NBA), a pigment molecule in mushrooms known to accumulate Cs . A numerical two-step approach, by Ota
. A numerical two-step approach, by Ota  , is employed to examine its alkali-metal-cation complexation selectivity in aqueous solutions. Applying it to the neutral, di- and tetra-deprotonated NBAs, we confirm that the complexation selectivity on Cs
, is employed to examine its alkali-metal-cation complexation selectivity in aqueous solutions. Applying it to the neutral, di- and tetra-deprotonated NBAs, we confirm that the complexation selectivity on Cs emerges only in high pHs, in which the di-protonated NBA dominates, in agreement with experimental results. This is the first demonstration of the approach for a biological molecule whose selectivity is known to be anomalous.
emerges only in high pHs, in which the di-protonated NBA dominates, in agreement with experimental results. This is the first demonstration of the approach for a biological molecule whose selectivity is known to be anomalous.
Ota, Yukihiro; Ruiz-Barragan, S.*; Machida, Masahiko; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics Letters, 648, p.119 - 123, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:19.3(Chemistry, Physical)We developed an interface program between a program suite for an automated search of chemical reaction pathways, GRRM, and a program package of semiempirical methods, MOPAC. A two-step structural search is proposed as an application of this interface program. A screening test is first performed by semiempirical calculations. Subsequently, a reoptimization procedure is done by ab initio or density functional calculations. We apply this approach to ion adsorption on cellulose. The computational efficiency is also shown for a GRRM search. The interface program is suitable for the structural search of large molecular systems for which semiempirical methods are applicable.
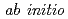 simulations
simulationsRuiz-Barragan, S.*; Ishimura, Kazuya*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics Letters, 646, p.130 - 135, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:55.76(Chemistry, Physical)A hierarchical parallelization has been implemented in a new unified code PIMD-SMASH for 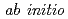 simulation where the replicas and the Born-Oppenheimer forces are parallelized. It is demonstrated that ab initio path integral molecular dynamics simulations can be carried out very efficiently for systems up to a few tens of water molecules. The code was then used to study a Diels-Alder reaction of cyclopentadiene and butenone by ab initio string method. A reduction in the reaction energy barrier is found in the presence of hydrogen-bonded water, in accordance with experiment.
simulation where the replicas and the Born-Oppenheimer forces are parallelized. It is demonstrated that ab initio path integral molecular dynamics simulations can be carried out very efficiently for systems up to a few tens of water molecules. The code was then used to study a Diels-Alder reaction of cyclopentadiene and butenone by ab initio string method. A reduction in the reaction energy barrier is found in the presence of hydrogen-bonded water, in accordance with experiment.
Honda, Tomohiro*; Minoshima, Yusuke*; Yokoi, Yuki*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics Letters, 625, p.174 - 178, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:19.29(Chemistry, Physical)Electron attachment dynamics to the guanine-cytosine (G-C) base pair in the gas phase isstudied using DFT and molecular dynamics. The potential energy surface of the G-C anion isconstructed with the empirical-valence-bond method using force-field information obtained from long-range corrected DFT calculations. Ring-polymer molecular dynamics simulations predict that theinitial dipole-bound anion readily converts into the valence-bound anion within 0.1 ps and proton-transfer occurs subsequently within 10 ps. The same process was found in classical simulations, buton a much slower time scale. This result suggests that nuclear quantum effects are important inunderstanding DNA damage by low-energy electrons.
Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro
Chemical Physics Letters, 594, p.64 - 68, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.21(Chemistry, Physical)Structures of mono-layered silicon on a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) have been investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES). For the Si K-edge XANES spectrum of the 0.15 mono-layered film, two distinct peaks were observed, which were assigned to the resonant excitations from the Si 1s into the valence unoccupied orbitals with 
 and
and 
 characters. On the basis of the polarization dependences of the peak intensities, it was concluded that a part of the Si film lies flat on the HOPG surface, which supports the existence of two-dimensional graphene-like structure in mono-layered silicon.
characters. On the basis of the polarization dependences of the peak intensities, it was concluded that a part of the Si film lies flat on the HOPG surface, which supports the existence of two-dimensional graphene-like structure in mono-layered silicon.
Shimada, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Taishi*; Minami, Hirotake*; Ukai, Masatoshi*; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari; Fukuda, Yoshihiro*; Saito, Yuji
Chemical Physics Letters, 591, p.137 - 141, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.36(Chemistry, Physical)Murakami, Hiroshi; Toyota, Yuji*; Nishi, Takaki*; Nashima, Shigeki*
Chemical Physics Letters, 519-520, p.105 - 109, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:57.65(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 -Co compound/Ni bilayer structure
-Co compound/Ni bilayer structureMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Avramov, P.; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*
Chemical Physics Letters, 511(1-3), p.68 - 72, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.38(Chemistry, Physical)X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectroscopy was employed to investigate the electronic and magnetic structures of the bilayers of a C -Co compound and Ni. A few -several nm thick C
-Co compound and Ni. A few -several nm thick C -Co compound layers on the Ni(111) surface are found to show intense XMCD signals attributed to the localized Co d-spins only with the remanent magnetization of Ni layer. It is suggested that the region of the C
-Co compound layers on the Ni(111) surface are found to show intense XMCD signals attributed to the localized Co d-spins only with the remanent magnetization of Ni layer. It is suggested that the region of the C -Co compound within 3 nm from the interface is ferromagnetically coupled with Ni due to the indirect exchange interaction mediated by C
-Co compound within 3 nm from the interface is ferromagnetically coupled with Ni due to the indirect exchange interaction mediated by C , probably relevant to the interlayer charge transfer.
, probably relevant to the interlayer charge transfer.
 LC-DFT study of graphene, multilayer graphenes and graphite
LC-DFT study of graphene, multilayer graphenes and graphiteAvramov, P.; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
Chemical Physics Letters, 508(1-3), p.86 - 89, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.62(Chemistry, Physical) C; Monte-Carlo simulations
C; Monte-Carlo simulationsSanguanmith, S.*; Muroya, Yusa*; Meesungnoen, J.*; Lin, M.; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Mirsaleh Kohan, L.*; Guzonas, D. A.*; Stuart, C. R.*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*
Chemical Physics Letters, 508(4-6), p.224 - 230, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:82.21(Chemistry, Physical)Our Monte-Carlo modeling of the high-temperature radiolysis of water by low-LET radiation was re-examined in an attempt to reconcile our computed 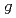 -values of the various radiolytic products with recently re-assessed experimental data up to 350
-values of the various radiolytic products with recently re-assessed experimental data up to 350 C. The inclusion in our simulations of the abrupt drop in the rate constant for the self-reaction of hydrated electron above 150
C. The inclusion in our simulations of the abrupt drop in the rate constant for the self-reaction of hydrated electron above 150 C led us to re-evaluate the temperature dependence of certain parameters intervening in the physicochemical stage of the radiolysis. A very good agreement was found between model and experiment. The importance of the reaction of H atoms with water in the unexplained yield of H
C led us to re-evaluate the temperature dependence of certain parameters intervening in the physicochemical stage of the radiolysis. A very good agreement was found between model and experiment. The importance of the reaction of H atoms with water in the unexplained yield of H above 200
above 200 C was also briefly discussed.
C was also briefly discussed.
Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Sugawara, Shuichi*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Chemical Physics Letters, 496(1-3), p.14 - 19, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:67.43(Chemistry, Physical)Full-dimensional path-integral molecular dynamics simulations were performed to determine whether the double proton transfer tautomerization of porphycene is a concerted or a stepwise process. It was found that double proton transfer occurs dominantly through the concerted pathway via the second-order saddle point structure and that contribution of the stepwise mechanism increases with a temperature increase. Nuclear quantum effects play essential roles in determining the proton transfer mechanism.
Ukai, Masatoshi*; Yokoya, Akinari; Fujii, Kentaro; Saito, Yuji
Chemical Physics Letters, 495(1-3), p.90 - 95, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:38.16(Chemistry, Physical)The X-ray absorption of nucleotides (adenosine-5'-monophosphate, guanosine-5'-monophosophate, and cytidine-5'-monophosophate) are measured in both water solutions and thin solid films at X-ray energies near the nitrogen K-edge in the "water-window" region. Each spectrum corresponds to the selective excitation of a nucleobase site in a nucleotide, and thus has features similar to the spectrum of the corresponding nucleobase. An additional new peak in the energy region of the nitrogen 1s
 * resonance is observed for each nucleotide. No significant difference between the water solutions and thin solid films is found, which might be attributable to the hydrophobic properties of a nucleobase in a nucleotide.
* resonance is observed for each nucleotide. No significant difference between the water solutions and thin solid films is found, which might be attributable to the hydrophobic properties of a nucleobase in a nucleotide.
Kasajima, Tatsuya; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Matsuoka, Leo; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Chemical Physics Letters, 485(1-3), p.45 - 48, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.01(Chemistry, Physical) O)
O)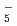 and (D
and (D O)
O)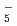
Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Motegi, Haruki*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics Letters, 482(4-6), p.195 - 200, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:29.21(Chemistry, Physical)Path-integral molecular dynamics simulations have been performed for water anion clusters,(H O)
O)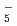 and (D
and (D O)
O)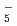 , on the basis of a semiempirical one-electron pseudopotential polarization model. Due to larger zero-point vibrational amplitudes for H atoms than that of D atoms, hydrogen-bond lengths in the (H
, on the basis of a semiempirical one-electron pseudopotential polarization model. Due to larger zero-point vibrational amplitudes for H atoms than that of D atoms, hydrogen-bond lengths in the (H O)
O)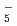 cluster are slightly larger than those in (D
cluster are slightly larger than those in (D O)
O)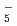 . The distribution of the vertical detachment energies for (H
. The distribution of the vertical detachment energies for (H O)
O)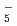 also show a broader feature than that for (D
also show a broader feature than that for (D O)
O)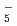 . The present simulations thus demonstrate the importance of nuclear quantum effects in water anion clusters.
. The present simulations thus demonstrate the importance of nuclear quantum effects in water anion clusters.